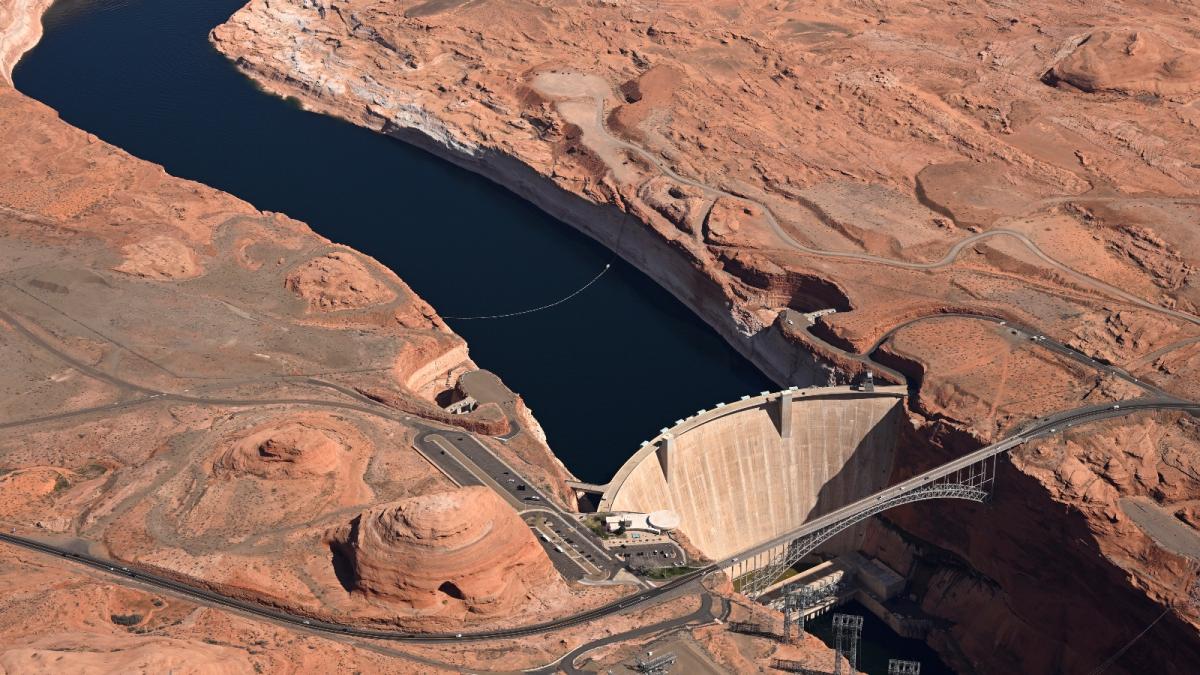
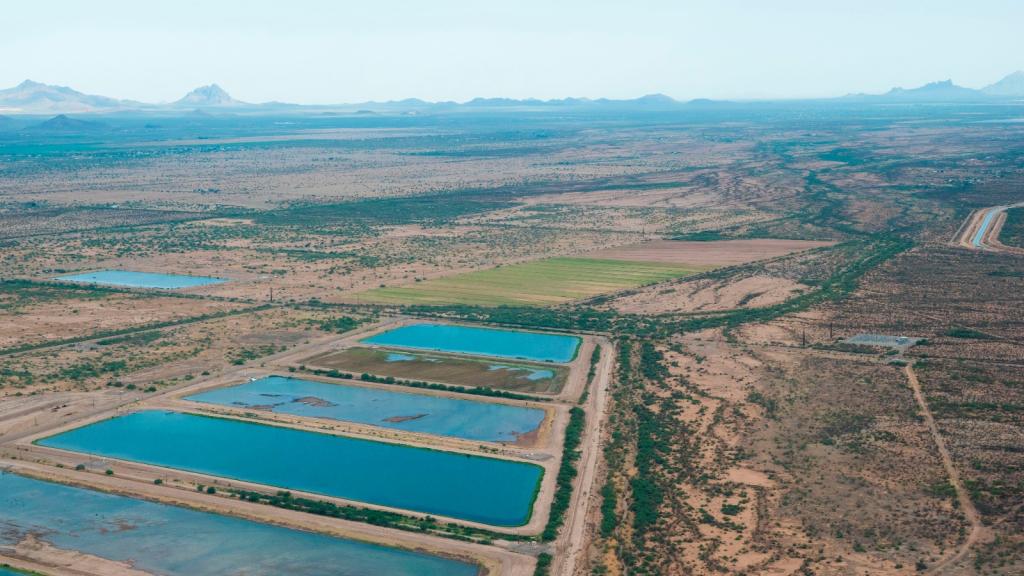
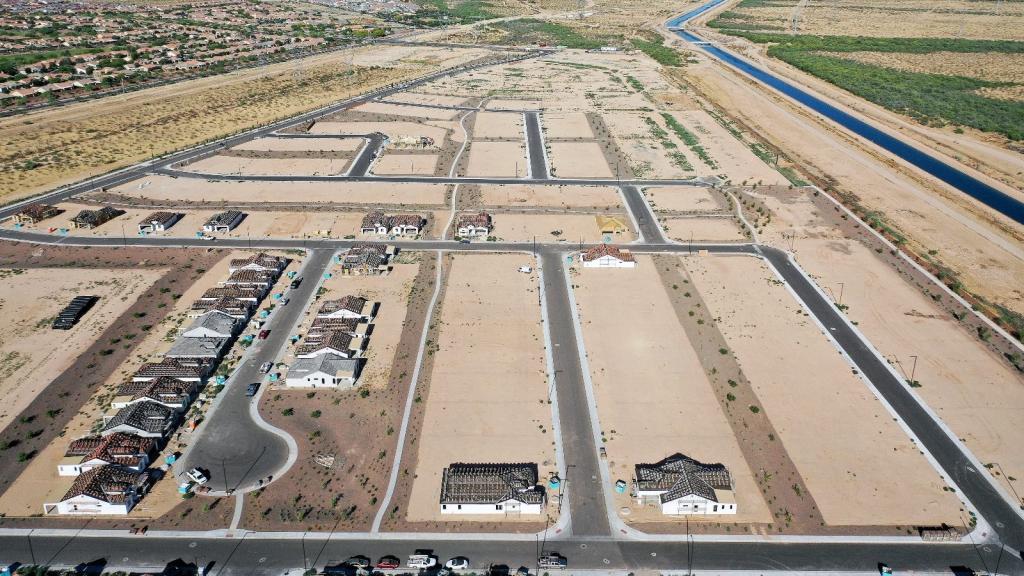
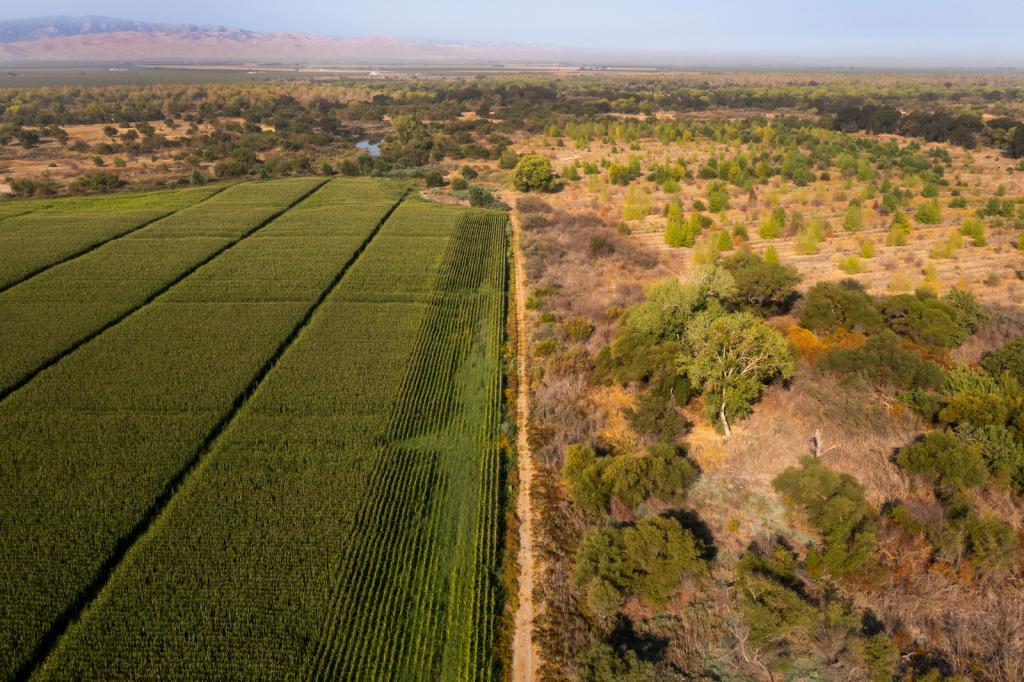
There are three main forces driving the conflict on the Colorado River. The first is an outdated legal system that guarantees more water to seven Western states — Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming — than is actually available in the river during most years. The second is the exclusion of Native American tribes from this legal system, which has deprived many tribes of water usage for decades. The third is climate change, which is heating up the western United States and diminishing the winter snowfall and rainwater that feed the river.
The states and tribes within the Colorado River basin have been fighting over the waterway for more than a century, but these three forces have come to a head over the past few years. As a severe drought shriveled the 1,450-mile river in 2022, negotiators from the seven states crisscrossed the country haggling over who should have to cut their water usage, and how much. As the arguments dragged on, the Biden administration chastised states for letting the water levels in the river’s two main reservoirs fall to perilous lows. The Navajo Nati... Read more